Inflammatory Bowel Disease
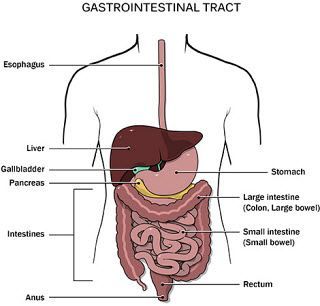
Bowel Anatomy
The bowel is found at the lower part of the digestive system and passage along which food passes through the body from mouth to anus during digestion.
The bowel is part of the alimentary canal below the stomach and a hollow tube.
The digestive system processes all our food and breaks it down into nutrients for the body.
It also removes any solid waste matter from the body in the form of faeces or stools.
The bowel is divided into two categories:
- The small bowel (or small intestine) is where food is digested, and nutrients are absorbed from what we eat.
- The large bowel (or colon and rectum) is where water is absorbed from the digested food and forms the stools.
Non-Cancer Bowel Diseases
Most problems relating to bowel cancer are associated with the large bowel. While the small bowel can be obstructed, this is uncommon.
Other conditions can affect the bowel and cause similar symptoms to cancer.
With the proper treatment, many of these conditions can be controlled. These include:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Piles (haemorrhoids) and
- Other infections
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) refers to a group of conditions that cause long-lasting inflammation in the digestive tract. This inflammation is caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking the digestive tract as if it were a foreign threat involving foods, bacteria, and other substances. This attack increases white blood cells in the intestinal lining, causing persistent inflammation.
The two main types of IBD are:
- Ulcerative Colitis: This affects only the colon and rectum, where inflammation and ulcers form along the innermost lining.
- Crohn's Disease: This can occur anywhere in the digestive tract, often affecting deeper bowel wall layers.
Both conditions can cause symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhoea, weight loss, and fatigue. Managing IBD usually involves treatments that reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and improve quality of life.
How Does Inflammatory Bowel Disease Affect Health?
Inflammatory Bowel Disease can impact the anatomy of the digestive system, causing inflammation, ulceration, and scarring in the gut. It can also lead to various health issues, including malnutrition, fatigue, anaemia, and even colon cancer.
Inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease should not be confused with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), a disorder that affects the colon’s muscle contractions. Intestinal inflammation is not a symptom of irritable bowel syndrome, a much less severe disease than ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
What are the Causes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
The exact causes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease are still unknown. Still, researchers believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors can contribute to the development of the disease.
- Genetics plays a vital role in the development of IBD, with up to 20% of people with IBD having a family history of the condition.
- Environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle choices, can also contribute to the development of the disease.
- Finally, the immune system also plays a role in IBD, with the body's immune system mistakenly attacking the gut lining and causing inflammation.
How is Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosed?
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is diagnosed through medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Medical history includes asking the patient about their symptoms, family history of IBD, and other relevant medical conditions.
- A physical examination may involve a digital rectal exam, abdominal exam, and other tests as required.
- Diagnostic tests for IBD include blood tests, stool tests, endoscopy, and colonoscopy, as well as imaging tests such as CT scans and MRIs. These tests can help identify inflammation, ulcers, and other abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Sometimes, a biopsy may be taken during an endoscopy or colonoscopy to help confirm a diagnosis of IBD. A biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the lining of the digestive tract and examining it under a microscope.
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon and rectum.
Who is Most at Risk for Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative Colitis can affect people of any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed in people between 15 and 30 years old. The condition is more common in women than men. People with a family history of ulcerative colitis or other inflammatory bowel diseases are also at increased risk for the condition.
What are the Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis?
Common symptoms of the condition include:
- Diarrhoea, often with blood or pus
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Rectal bleeding
- The urgency to have a bowel movement
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
In severe cases, ulcerative colitis can lead to complications such as bowel obstructions, perforations, and an increased risk of colon cancer.
Treatments for Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes.
- Medications to treat the condition include anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and antibiotics.
- Lifestyle changes such as dietary changes and stress management can also help manage symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis.
- In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected part of the colon and rectum.
Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a condition of chronic inflammation that can potentially involve the entire digestive or gastrointestinal tract. Often, however, it affects the end of the small bowel and the beginning of the large bowel.
In Crohn's disease, all layers of the intestine may be involved, and there can be normal healthy bowel between patches of diseased bowel.
Who is Most at Risk for Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s Disease can affect people of any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed in people between the ages of 15 and 30. The condition is more common in women than men. People with a family history of Crohn’s Disease or other inflammatory bowel diseases are also at increased risk for the condition.
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
Commonly symptoms of Crohn’s disease include:
- Persistent diarrhoea (loose, watery, or frequent bowel movements)
- Cramping abdominal pain
- Fever
- Rectal bleeding (at times)
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Fatigue
- Symptoms can also affect the Joints, eyes, skin, and liver
The most common complication of Crohn’s disease is blockage of the intestine due to swelling and scar tissue.
Symptoms of blockage include cramping, pain, vomiting, and bloating. Another complication is sores or ulcers within the intestinal tract. Sometimes, these deep ulcers turn into tracts—called fistulas.
Crohn’s Disease patients have an increased risk of colon cancer.
Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
Treatment for Crohn’s Disease typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes.
- Medications to treat the condition include anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and antibiotics.
- Lifestyle changes such as dietary and stress management can also help manage Crohn’s disease symptoms.
- Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to remove the affected part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Surgery for Crohn’s Disease
While surgery is not a cure for Crohn's disease, it should enable patients to eat and drink without pain and stop taking Crohn's drugs.
Surgery for Crohn's disease involves the removal of the diseased bowel. Most long-term sufferers of Crohn's disease resolve their condition with surgery.
While symptoms may recur over time, and many patients can require a second procedure, this typically will lead to a long-term solution.
What if Inflammatory Bowel Disease is Untreated?
Leaving Inflammatory Bowel Disease untreated can lead to a range of serious consequences. In addition to severe symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhoea, untreated IBD can lead to complications such as malnutrition, dehydration, and anaemia. Long-term inflammation can also increase the risk of colon cancer. Finally, untreated IBD can significantly impact a person's quality of life, leading to social isolation and depression.
If you are experiencing symptoms of IBD, it is essential to speak to your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.